Demand
Last Updated On -08 Mar 2025

The demand is the quantity of goods or services that consumers are willing or able to purchase in a given period. Demand acts as a driving force in the market, influencing the price and production of goods. It is an important economic concept; a consumer's needs or wants decide the product's nature. It offers businesses an opportunity to stay innovative and young minds to get into entrepreneurship and create a revolution in the market.
Demand presents the market with challenges and chances, which, in return, provide consumers with unique products and services.
Types of Demand
Consumer behaviour, market conditions, and the relationship with other goods and services determine the types of demand.
The main types of demand are:
1. Individual & Market Demand
- Individual demand: Demand for a product demanded by a single consumer.
- Market demand: Demand for a product from all consumers in the market.
2. Direct & Derived Demand
- Direct demand: The goods that are directly demanded and consumed by the consumer
- Derived demand: The goods demanded and consumed by other products, such as demand for steel, increase when the demand for cars rises.
3. Elastic & Inelastic Demand
- Elastic demand: Big change in demand through small price change
- Inelastic demand: No significant change in demand after price changes
Key Factors affecting Demand
The demand for a product or service depends on several factors. These factors decide the annual sale of a product and the company's financial performance. The factors can be the need or want of the consumer or an external factor influencing it.
The key factors affecting demand are:
- Price of the product
- Income of the consumer
- Price of related goods
- Consumer preferences
- Future predictions of the price
Law of Demand
“As the price of a good increase, the quantity demanded increases, assuming all the other factors remain constant, " as the law of demand states.
- Inverse Relationship: The price and demand move in opposite directions
- Demand curve: The slope moves from left to right
Demand Curve
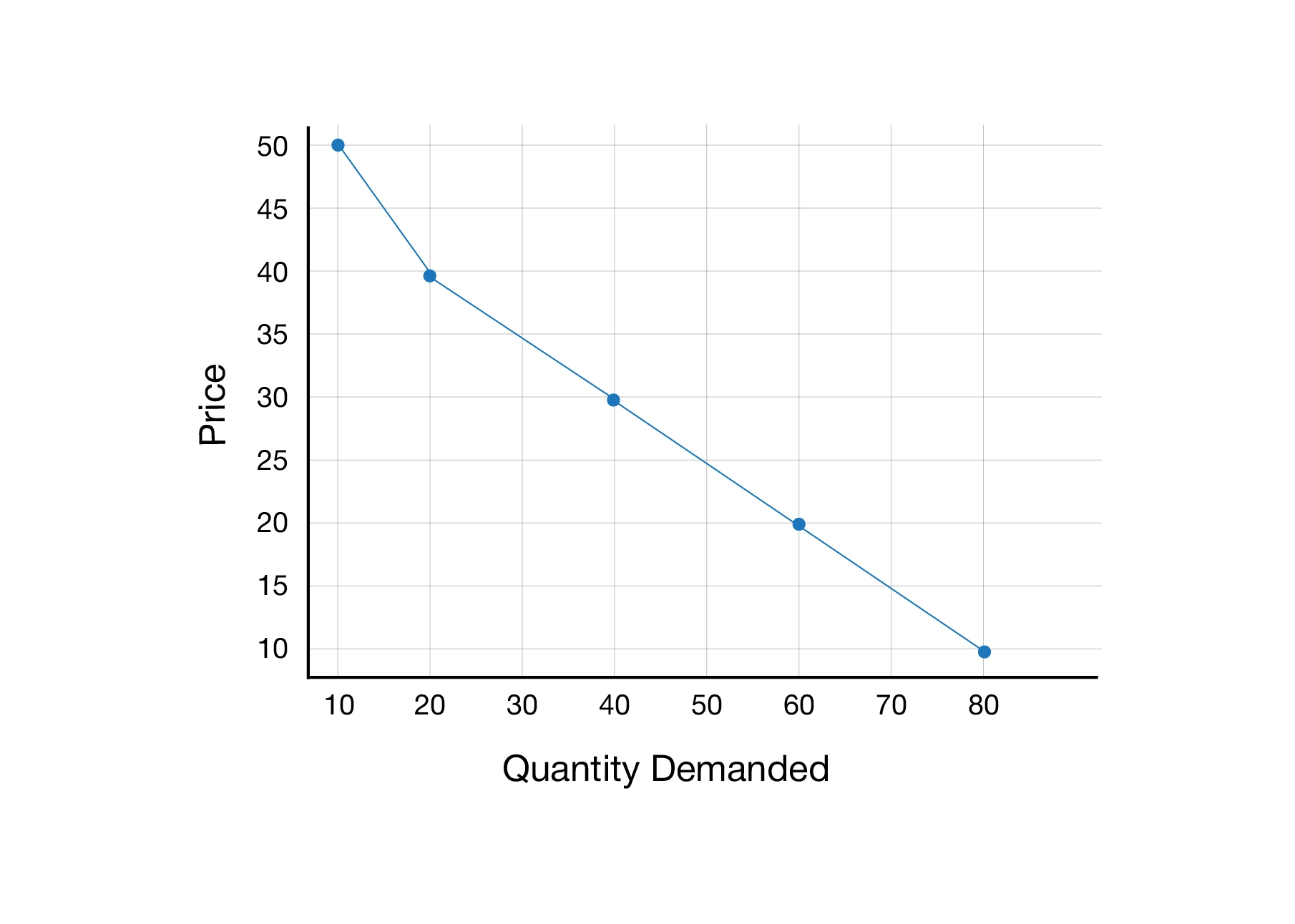
The demand curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the price and quantity of the goods consumers demand. In simpler terms, if the cost of a product falls, the demand for the product increases.
- Price and demand have an inverse relationship, i.e., with the price increase, the demand decreases.
- The demand curve slopes downward from left to right, indicating a negative relationship.
- The normal demand curve is a downward slope representing the law of demand: decrease in price, increase in demand. The slope is negative, moving from the top left to the bottom right corner.
Significance of the Demand
The demand curve plays an important role in influencing the prices of a certain product and the product planning by the businesses.
The significance of the demand is as follows:
- Helps in price determination
- Influences product planning
- Determines ongoing market trends
- The higher demand for a product leads to more production and employment.
See Also
- 14 principles of Henri Fayol's management
- What is commerce?
- Organized and Unorganized sector
- Demat Account
Want to learn more about trending and informational topics in commerce? Check out the latest Commerce Blogs and stay up to date!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the relation between demand and supply?
The demand and supply have a direct relationship. When demand increases, supply increases naturally. This leads to an increase in the pricing of the products and a decrease in the stock for the customers.
What is the law of demand?
“As the price of a good increase, the quantity demanded increases, assuming all the other factors remain constant, " as the law of demand states.
- Inverse Relationship: The price and demand move in opposite directions
- Demand curve: The slope moves from left to right
For example, if the price of a smartphone decreases, more people will buy it.
How does the future price expectation affect demand?
When consumers expect the pricing to increase in the future, the demand for the product will go up in the present time. Conversely, if the pricing is likely to drop in the future, there is a delay in the demand for the product.












































































































































































































































.webp)











































